What is Cannabigerol? The Role of CBG in Cannabis
CBG 101: What to know about the cannabinoid you haven’t met yet (but should). More people than ever can tell you the difference between THC and CBD—the two most prominent and famous cannabinoids found within the cannabis plant. These two have earned their place in the spotlight: THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is responsible for the most famous effects in marijuana, including a stimulated appetite, altered sense of time, and euphoric high. CBD, or cannabidiol, is notable for its calming, soothing, pain-reducing powers.
More people than ever can tell you the difference between THC and CBD—the two most prominent and famous cannabinoids found within the cannabis plant. These two have earned their place in the spotlight: THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is responsible for the most famous effects in marijuana, including a stimulated appetite, altered sense of time, and euphoric high. CBD, or cannabidiol, is notable for its calming, soothing, pain-reducing powers.
THC and CBD may be famous, but they’re far from the only cannabinoids found within the cannabis plant. In fact, scientists have already identified over a hundred different cannabinoids, each offering its own effects. A third cannabinoid with potential therapeutic benefits is cannabigerol, or CBG.
CBG: The “Stem Cell Cannabinoid”
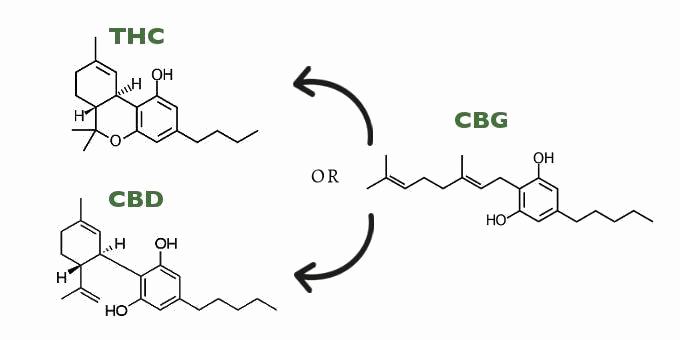
CBG deserves more credit than it gets: all cannabinoids actually begin their lives as cannabigerol. That’s what gives cannabigerol its many nicknames: the stem cell cannabinoid, the parent cannabinoid, and the mother cannabinoid. As the cannabis grows, most CBG converts to other cannabinoids, especially THC and (in some strains) CBD. By the time cannabis is harvested for recreational marijuana, for example, CBG is only a tiny percentage of the cannabinoid ratio.
That said, certain strains of industrial hemp are rich in CBG, as well as its acidic form, cannabigerolic acid. Many states require by law that industrial hemp—which is used for material goods like fabric and compostable plastic—must contain less than 0.3 percent THC. As a result, these cannabis strains develop into plants with a higher ratio of CBG and CBD. With a potentially huge supply of CBG available from industrial hemp, researchers are keen on learning just what CBG can do.
Q: What is CBG?
A: CBG, short for cannabigerol, is a cannabinoid that may have some benefits for human health. CBG is considered a parent cannabinoid because all other cannabinoids start as CBG, until they synthesize into other types of cannabinoids—mainly THC and CBD. CBG does not have psychoactive effects, unlike THC.
How Does CBG Actually Work?
All cannabinoids interact with the body by triggering receptors in the body, particularly in the central nervous system and immune system. The main groups of receptors are appropriately named CB1 receptors and CB2 receptors (in which CB stands for cannabinoid). When a CB receptor is activated, it alters normal neurotransmission—the body’s communication system—and that’s what creates the side effects of inhaling or consuming marijuana.
CB1 receptors sit on the surface of nerves, particularly in the brain and spinal cord, and this is the reason cannabinoids can alter behavior, cognition, and coordination. CB2 receptors are mostly found in immune tissues, which give cannabinoids their medical benefits.
Q: How does CBG work?
A: Like THC, CBG works by interacting with CB1 receptors (located primarily in the central nervous system) and CB2 receptors (located primarily in the immune tissue). This alters normal neurotransmission in the body and creates different effects.
CBG vs. THC
The CB1 and CB2 receptors are often associated with THC, but this famous cannabinoid isn’t the only one fond of these receptors: CBG also appears to act on the CB1 and CB2 receptors. (CBD, on the other hand, engages with other receptors in the body.)
The fact that CBG engages with CB1 receptors in the central nervous system could explain why CBG shares some traits with THC, such as the ability to stimulate appetite. You have CB1 receptors in the hypothalamus, a part of the brain that regulates hormones in the brain that control biologic needs like appetite, sex drive, thirst, and temperature regulation. When THC or CBG activates these receptors, it can alter hormones that increase your sense of hunger.
That doesn’t mean CBG can do everything THC can; obviously, it doesn’t cause a high, and it doesn’t make you clumsy or slow your reaction time. This highlights the unique properties and actions of the individual cannabinoids, despite their similarities.

CBG shares some traits with THC, such as the ability to stimulate appetite.
The Potential Health Benefits of CBG
As with CBD, the lesser-known CBG is gaining interest thanks to the fact that it’s non-psychotropic, meaning it doesn’t cause a high. This make CBG an attractive therapeutic option for people who want the potential health benefits of cannabis without the psychoactive effects.
Although CBG was first discovered in 1964, the research on CBG and its effects is still in its youth. However, researchers have noted a few examples of what cannabigerol is capable of:
• Stimulating appetite: THC usually gets the credit for stimulating appetite, which is a useful treatment for people undergoing chemotherapy, for example. A 2016 study in Psychopharmacology noted that a cannabis extract without any THC still managed to rev up appetites. The researchers found that rats given CBG concentrate more than doubled their consumption.
• Preserving cognitive function: Most adults experience some extent of cognitive decline as they age, which can be severe and result in dementia. A 2015 study in Neurotherapeutics found that CBG improved two key markers of cognitive health: motor skills and neuron function. Additionally, CBG has been shown to reduce neuroinflammation—or inflammation in the brain.
• Treating gastrointestinal problems: You have both CB1 and CB2 receptors in the layers of your intestines. Because of this, cannabinoids like CBG can relieve pain and inflammation in the intestinal tract, and researchers believe it could be beneficial in treating inflammatory bowel disease, or IBD. A 2013 study in Biochemical Pharmacology journal found that CBG actually improved the weight-to-length ratio of the colon, which is an indirect marker of inflammation. That means CBG didn’t just mask symptoms; it reduced the underlying inflammation.
• Treating multiple sclerosis (MS): MS is an autoimmune condition that causes inflammatory attacks on the central nervous system. Since CB1 receptors are located all over the central nervous system, it makes sense that cannabis has been such a groundbreaking treatment for the tricky condition. A 2012 study found that a derivative of CBG treated MS by protecting neurons from damage and reducing the release of inflammatory substances.
• Reducing general inflammation: Most of the inflammation-based research on CBG has focused on inflammation in the brain and in the bowel. However, there’s evidence CBG’s anti-inflammatory effects go beyond your mind and gut. One 2011 study found that six of the major cannabinoids—including CBG—inhibited activity of cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes, which produce inflammatory prostaglandins. In other words, CBG and other cannabinoids can reduce the release of inflammatory substances.
Q: What are the benefits of CBG?
A: Research on the medical benefits of CBG is still young, but there is some evidence that CBG may help reduce inflammation, stimulate appetite, treat gastrointestinal disorders like inflammatory bowel disease, treat multiple sclerosis, and preserve cognitive function.

CBG has the potential health benefits of cannabis without the psychoactive effects.
How Do You Use CBG?
While you can get small percentages of CBG in some standard marijuana products, you’ll need to look elsewhere for a greater concentration of cannabigerol. Remember, in most strains of recreational marijuana, CBG molecules are converted to THC, leaving very little CBG in the final product.
The best way to get CBG is in oil or isolate form. As the name suggests, CBG isolate is an isolated form of CBG, extracted from cannabis plants. Instead of inhaling isolate, you can simply consume it.
CBG oil usually comes in tincture form. Typically, you take CBG oil by placing and holding the oil under the tongue (where it is absorbed into the bloodstream). This is the most effective way to get CBG to the CB receptors because it bypasses the digestive system. That said, you can also add CBG oil to food or drinks, but keep in mind that some CBG will get lost in the digestion process. Finally, for topical use, you can apply CBG oil directly to the skin.
Q: What is CBG oil?
A: CBG oil is a concentrate of cannabigerol molecules. It usually comes in tincture form and can be taken sublingually (under the tongue), by adding it to food or drink, or by applying it directly to the skin.
The Future of CBG
There is still a lot to learn about cannabigerol, but interest is high and research is increasing. One thing is for sure: non-psychoactive cannabinoids like CBG offer major potential for natural treatment of human ailments. Continuing research could reveal even more benefits that are yet unknown.

It’s good to know that CBG can give people the therapeutic benefits of CBD without any of the psychoactive side effects. I know a ton of people who use CBD as a way to help with their anxiety or their depression. I’ll talk to them about maybe using CBG so they aren’t getting high but are still getting the help they need.